Aşağıdaki gibi 2 ayrı sınıf oluşturuyoruz ve kodları giriyoruz.
Yazılım Nedir?
Yazılım, temelde bilgisayara nasıl çalışacağını söyleyen komutlar ve veriler bütünüdür.
Bilişim Nedir?
Bilişim, bir anlamda “paylaşmak” demektir. Bilgisayar ve yazılımların insanların ihtiyaçlarına göre düzenlendiği uçsuz bucaksız bir platformdur.
Bilgisayar Mühendisliği Nedir?
Bilgisayar mühendisliği, bilgisayar ve bilgisayar tabanlı sistemlerin yazılım ve donanımlarının tasarımı, gerçekleştirimi ve yönetimi ile ilgilenen bir bilim dalıdır.
Mühendislik Nedir?
Mühendis; teknik, matematiksel ve sosyal veriler ışığında insanların kullanımına yönelik yeni sistemler üretme ve geliştirme ile sorumludur.
Bilim ve Teknoloji İlişkisi Nedir?
Teknoloji, bilimsel keşiflerin uygulamalarını sağlarken, bilim teknolojik ilerlemelerin temelini oluşturan bilgiyi sunar.
29 Eylül 2023 Cuma
C#'DA VIRTUAL/OVERRIDE
21 Eylül 2023 Perşembe
C#'DA DÖNGÜLER
FOR DÖNGÜSÜ
for (int i = 0; i <= 7; i++)
Console.WriteLine("TALO");
Console.ReadLine();
int sonuc = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 7; i++)
{
sonuc += i;
Console.WriteLine("Sonuç : " + sonuc);
}
Console.ReadLine();
int i = 0, x = 0;
for (; i < dizi.Length;)
{
x = dizi.Length;
i++;
}
Console.WriteLine(x - i);
Console.WriteLine(x);
Console.WriteLine(i);
Console.ReadLine();
for (/*dışarıda tanımladık*/; i < 3;/*içeride tanımladık*/)
{
Console.WriteLine("Döngü içi : " + i);
i++;
}
Console.WriteLine("Döngü dışı : " + i);
Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine("AA");
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++)
{
if (i != 3)
{
Console.WriteLine("Değer : " + i);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Hediye kazandınız!");
}
}
for (int i = 20; i >= 0; i--)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
Console.ReadLine();
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++)
{
if (i % 5 == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("Beşe bölünebilen : " + i);
bolunebilen++;
}
else if (i % 5 != 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("Beşe bölünemeyen : " + i);
bolunemeyen++;
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Bölünebilen Sayı Toplam : " + bolunebilen);
Console.WriteLine("Bölünemeyen Sayı Toplam : " + bolunemeyen);
Console.ReadLine();
int sayi = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("Kaça : ");
int kacaBol = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
int bolunebilen = 0, bolunemeyen = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= sayi; i++)
{
if (i % kacaBol == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("Bölünebilen : " + i);
bolunebilen++;
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Bölünemeyen : " + i);
bolunemeyen++;
}
}
Console.WriteLine(Environment.NewLine);
Console.WriteLine("******************************");
Console.WriteLine(Environment.NewLine);
Console.WriteLine(bolunebilen + " adet bölünebilen sayı bulundu!");
Console.WriteLine(bolunemeyen + " adet bölünemeyen sayı bulundu!");
Console.ReadLine();
{
}
Console.ReadLine();
{
Console.WriteLine("Deep I/O");
}
Console.ReadLine();
while (i <= 7)
{
Console.WriteLine("Deep I/0 : " + i);
i++;
}
Console.ReadLine();
int i = 1;
while (i <= 100)
{
if (i % 5 == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("Beşe bölünebilen : " + i);
}
else if (i % 5 != 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("Beşe bölünemeyen : " + i);
}
i++;
}
Console.WriteLine("Bölünebilen Sayı Toplam : " + bolunebilen);
Console.WriteLine("Bölğnemeyen Sayı Toplam : " + bolunemeyen);
Console.ReadLine();
int sayi = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("Kaça : ");
int kacaBol = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
int bolunemeyen = 0, bolunebilen = 0, i = 1;
while (i <= sayi)
{
if (i % kacaBol == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("Bölünebilen : " + i);
bolunebilen++;
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Bölünemeyen : " + i);
bolunemeyen++;
}
i++;
}
Console.WriteLine(Environment.NewLine);
Console.WriteLine("******************************");
Console.WriteLine(Environment.NewLine);
Console.WriteLine(bolunebilen + " adet bölünebilen sayı bulundu!");
Console.WriteLine(bolunemeyen + " adet bölünemeyen sayı bulundu!");
Console.ReadLine();
{
Console.WriteLine("Deep I/O");
}
while (false);
int counter = 0, lenght = 0;
do
{
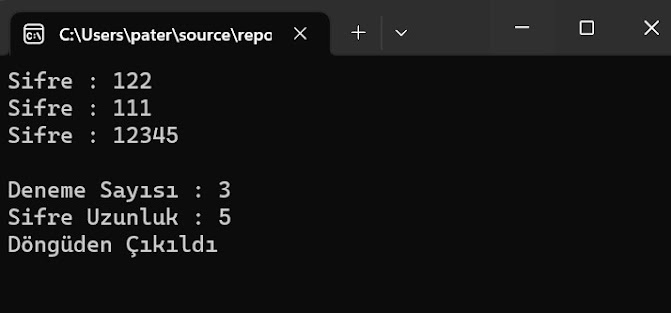
Console.Write("Şifre : ");
str = Console.ReadLine();
lenght = str.Length;
counter++;
} while (str != "12345");
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Deneme Sayısı : " + counter);
Console.WriteLine("Şifre Uzunluk : " + lenght);
Console.WriteLine("Döngüden Çıkıldı");
Console.ReadLine();
string mesaj = false ? "Doğru" : "Yanlış";
Console.ReadLine();
bool isValid = false;
string message = string.Empty;
string str = string.Empty;
do
{
Console.Write("Şifreyi Girin : ");
str = Console.ReadLine();
if (str == "12345")
{
isValid = true;
}
counter++;
if (counter >= 5)
{
break;
}
}
while (str != "12345");
Console.WriteLine("***************");
message = isValid ? " Başarılı" : " Başarısız";
Console.WriteLine("Giriş" + message);
Console.WriteLine("Parola Deneme Sayısı : " + counter);
Console.WriteLine("***************");
Console.ReadLine();
{
if (i < 9)
{
continue;
}
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
Console.WriteLine("Döngü Bitti!");
Console.ReadLine();
for (; ; )
{
Console.WriteLine("Bir Sayı Girin :");
sayi = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
if (sayi == 0)
break;
if (sayi == 5)
{
Console.WriteLine("Sayı Değeri 5");
continue;
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Döngü Bitti!");
Console.ReadLine();
foreach (int sayi in dizi)
{
Console.WriteLine(sayi);
}
Console.ReadLine();
18 Eylül 2023 Pazartesi
C#'DA KOLEKSİYONLAR
KOLEKSİYONLAR
JENERİK OLMAYAN KOLEKSİYONLAR
ArrayList Sehirler = new ArrayList();
Sehirler.Add("İstanbul");
Sehirler.Add("Ankara");
Sehirler.Add("İzmir");
Sehirler.Add("Antalya");
Sehirler.Add("Adana");
foreach (var sehir in Sehirler)
{
Console.WriteLine(sehir);
}
Sehirler.Add("İstanbul");
Sehirler.Add("Ankara");
Sehirler.Add("İzmir");
Sehirler.Add("Antalya");
Sehirler.Add("Adana");
Console.WriteLine("Count : " + Sehirler.Count);
Console.WriteLine("Capacity : " + Sehirler.Capacity);
Sehirler.Add("İstanbul");
Sehirler.Add("Ankara");
Sehirler.Add("İzmir");
Sehirler.Add("Antalya");
Sehirler.Add("Adana");
Console.WriteLine("Count : " + Sehirler.Count);
Console.WriteLine("Capacity : " + Sehirler.Capacity);
Console.WriteLine("Capacity : " + Sehirler.Capacity);
reach (var seh in sehirX)
liste.Add("İstanbul");
liste.Add(4.3M);
liste.Add(false);
liste.Add(new Program());
liste.Add("Mersin");
liste.Add("Ankara");
for (int i = 0; i < liste.Count; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(liste[i]);
}
Console.WriteLine(liste[1]);
Console.WriteLine(liste[1].GetType());
Console.WriteLine(Convert.ToDecimal(liste[1]) * Convert.ToDecimal(liste[1]));
Siniflar.Add("007", "Yazılım ve Veritabanı Uzmanlığı");
Siniflar.Add("008", "Sistem ve Ağ Uzmanlığı");
Siniflar.Add("005", "Ağ");
Siniflar.Add("001", "Ağ Uzmanlığı");
Siniflar.Add("021", "Uzmanlık");
foreach (DictionaryEntry sinif in Siniflar)
{
Console.WriteLine(sinif.Key);
}
Console.ReadLine();
Diller.Add("C");
Diller.Add("C++");
Diller.Add("C#");
foreach (var dil in Diller)
{
Console.WriteLine(dil);
}
Console.ReadLine();
Diller.Add("C");
Diller.Add("C++");
Diller.Add("C#");
for (int i = 0; i < Diller.Count; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(Diller[i]);
}
Diller.Add("C");
Diller.Add("C++");
Diller.Add("C#");
Console.WriteLine(Diller[Diller.Count - 1]);
Diller.Add("C");
Diller.Add("C++");
Diller.Add("C#");
Console.WriteLine(Diller[Diller.Count - 1]);
Diller.RemoveRange(1, 2);
foreach (var li in Diller)
{
Console.WriteLine(li);
}
Console.ReadLine();
C#'DA DİZİLER
DİZİLER
DİZİ TANIMLAMA
int[] dizi = new int[25];
bool[] dizi1 = new bool[10];
int[] dizi2;
dizi2 = new int[20];
DİZİYE DEĞER ATAMA
int[] strDizi = new int[3];
strDizi[0] = 5;
strDizi[1] = 7;
strDizi[2] = 9;
Console.WriteLine("Değer : " + strDizi[2]);
Console.ReadLine();
STRİNG DİZİ OLUŞTURMA
string[] sDizi = new string[4];
sDizi[0] = "T";
sDizi[1] = "A";
sDizi[2] = "L";
sDizi[3] = "O";
Console.ReadLine();
DİZİYİ OLUŞTURURKEN DEĞER ATAMA
string[] fString = { "ali", "ata", "bak" };
for(int i = 0; i < fString.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(fString[i]);
}
Console.ReadLine();
<------------------------>
string akademi = "TAYLAN";
for(int i = 0; i < akademi.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(akademi[i]);
}
Console.ReadLine();
<------------------------>
string[] sehirler = new string[3];
sehirler[0] = "İstanbul";
sehirler[1] = "Ankara";
sehirler[2] = "Adana";
Console.WriteLine(sehirler[2]);
Console.ReadLine();
<------------------------>
string[] sehirler = new string[3];
sehirler[0] = "İstanbul";
sehirler[1] = "Ankara";
sehirler[2] = "Adana";
for (int i = 0; i < sehirler.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(sehirler[i]);
}
Console.ReadLine();
<------------------------>
BİR ÖNCEKİ ÖRNEĞİ CHARLARINA AYIRMAK İSTERSEK
string[] sehirler = new string[3];
sehirler[0] = "İstanbul";
sehirler[1] = "Ankara";
sehirler[2] = "Adana";
for (int i = 0; i < sehirler.Length; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < sehirler[i].Length; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine(sehirler[i][j]);
}
Console.WriteLine("******");
}
Console.ReadLine();
<------------------------>
string[] sehirler = new string[3];
sehirler[0] = "İstanbul";
sehirler[1] = "Ankara";
sehirler[2] = "Adana";
for (int i = 0; i < sehirler.Length; i++)
{
if (sehirler[i] == "Ankara")
{
Console.WriteLine(sehirler[i] + " İli içerisinde dönülüyor.");
Thread.Sleep(2000);
for (int h = 0; h < sehirler[i].Length; h++)
{
if (h == 3)
{
Console.WriteLine("Aranılan bulundu : " + sehirler[i][h]);
}
}
}
}
Console.ReadLine();
ELEMAN SAYISINI KONSOLDAN ALARAK DİZİ OLUŞTURMA
Console.Write("Eleman Sayısı : ");
int sayi = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
int[] dizi = new int[sayi];
for (int i = 0; i < dizi.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(dizi[i]);
}
Console.ReadLine();
DİZİNİN HER İNDEKSİNDE BİR ÖNCEKİ İNDEKSİN 2 İLE ÇARPIMINI YAZMAK
int[] values = new int[3];
values[0] = 5;
values[1] = values[0] * 2;
values[2] = values[1] * 2;
Console.WriteLine(values[2]);
Console.ReadLine();
<------------------------>
int[] values = new int[3];
values[0] = 5;
for (int i = 1; i < values.Length; i++)
{
values[i] = values[i - 1] * 2;
}
Console.WriteLine(values[2]);
Console.ReadLine();
İKİ BOYUTLU DİZİLER
int[,] ikiBoyut =
{
{ 1,2 },
{ 3,4 },
{ 5,6 },
{ 7,8 }
};
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine(ikiBoyut[i,j]);
}
}
ikiBoyut[0, 1] = 20;
ikiBoyut[1, 0] = 30;
ikiBoyut[1, 1] = 40;
ikiBoyut[2, 0] = 50;
ikiBoyut[2, 1] = 60;
ikiBoyut[3, 0] = 70;
ikiBoyut[3, 1] = 80;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine(ikiBoyut[i, j]);
}
}
Console.ReadLine();
{
{ { 1,2 }, { 3,4 } },
{ { 5,6 }, { 7,8 } },
{ { 9,10 }, { 11,12 } },
{ { 13,14 }, { 15,16 } }
};
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < 2; k++)
{
Console.WriteLine(ucBoyut[i, j, k]);
}
}
}
ucBoyut[0, 0, 0] = 10;
ucBoyut[0, 0, 1] = 20;
ucBoyut[0, 1, 0] = 30;
ucBoyut[0, 1, 1] = 40;
ucBoyut[1, 0, 0] = 50;
ucBoyut[1, 0, 1] = 60;
ucBoyut[1, 1, 0] = 70;
ucBoyut[1, 1, 1] = 80;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < 2; k++)
{
Console.WriteLine(ucBoyut[i, j, k]);
}
}
}
Console.ReadLine();
{
new int[]{1,2,3,4,5,6 },
new int[]{1,2},
new int[]{1,2,3,4},
new int[]{1}
};
foreach (var jag in jagged)
{
foreach (var eleman in jag)
{
Console.WriteLine(eleman);
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
Console.ReadLine();
10 Eylül 2023 Pazar
C#'DA OPERATÖRLER
Operatörler, ve kullanımları aşağıdaki örneklerdeki gibidir.
ARİTMETİK OPERATÖRLER
int x = 10;int y = 5;
int result;
Console.WriteLine("x + y = {0}", x + y);
Console.WriteLine("x - y = {0}", x - y);
Console.WriteLine("x * y = {0}", x * y);
Console.WriteLine("x / y = {0}", x / y);
Console.ReadLine();
int m = 10;
int n = 4;
int p = m / n;
int x = m / n;
int y = m / n;
Console.WriteLine("p = {0} ", p);
Console.WriteLine("x = {0} ", x);
Console.WriteLine("y = {0} ", y);
Console.ReadLine();
int x, y, sonuc;
float fsonuc;
x = 7;
y = 5;
sonuc = x / y;
Console.WriteLine("x/y: {0}", sonuc);
fsonuc = (float)x / y;
Console.WriteLine("x/y: {0}", fsonuc);
fsonuc = x / (float)y;
Console.WriteLine("x/y: {0}", fsonuc);
fsonuc = (float)x / (float)y;
Console.WriteLine("x/y: {0}", fsonuc);
fsonuc = (float)(x / y);
Console.WriteLine("x/y: {0}", fsonuc);
Console.ReadLine();
double x = 13;
double y = 7;
double sonuc = x % y;
Console.WriteLine("x % y = {0}", sonuc);
Console.ReadLine();
double x = 10.57;
double y = 4.83;
double sonuc = x % y;
Console.WriteLine("x % y = {0}", sonuc);
Console.ReadLine();
int toplam = 0, fark = 0, carpim = 0, modulo = 0;
float bolum = 0;
int sayi1 = 10, sayi2 = 2;
toplam = sayi1 + sayi2;
fark = sayi1 - sayi2;
carpim = sayi1 * sayi2;
bolum = sayi1 / sayi2;
modulo = 3 % sayi2;
Console.WriteLine("sayı1 = {0}, sayı2 = {1}", sayi1, sayi2);
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("{0} + {1} = {2}", sayi1, sayi2, toplam);
Console.WriteLine("{0} - {1} = {2}", sayi1, sayi2, fark);
Console.WriteLine("{0} * {1} = {2}", sayi1, sayi2, carpim);
Console.WriteLine("{0} / {1} = {2}", sayi1, sayi2, bolum);
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("3 sayısı {0} ile bölününce {1} kalır", sayi2, modulo);
int x = 5;
Console.WriteLine("x = {0}", x);
Console.WriteLine("++x değeri = {0}", ++x);
Console.WriteLine("x = {0}", x);
x = 5;
Console.WriteLine("x++ değeri = {0}", x++);
Console.WriteLine("x = {0}", x);
Console.ReadLine();
int n = 35;
float x = 12.7f;
Console.WriteLine("n = {0} iken --n = {1} ve n = {2} olur.", n, --n, n);
Console.WriteLine("n = {0} iken ++n = {1} ve n = {2} olur.", n, ++n, n);
Console.WriteLine("n = {0} iken n-- = {1} ve n = {2} olur.", n, n--, n);
Console.WriteLine("n = {0} iken n++ = {1} ve n = {2} olur.", n, n++, n);
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("x = {0} iken --x = {1} ve x = {2} olur.", x, --x, x);
Console.WriteLine("x = {0} iken ++x = {1} ve x = {2} olur.", x, ++x, x);
Console.WriteLine("x = {0} iken x-- = {1} ve x = {2} olur.", x, x--, x);
Console.WriteLine("x = {0} iken x++ = {1} ve x = {2} olur.", x, x++, x);
Console.ReadLine();
int sayi = 0;
int onelArtim;
int onelEksim;
int sonalArtim;
int sonalEksim;
int pozitif;
int negatif;
sbyte bitNot;
bool logNot;
onelArtim = ++sayi;
Console.WriteLine("Önel-Artım: {0}", onelArtim);
onelEksim = --sayi;
Console.WriteLine("Önel-Eksim: {0}", onelEksim);
sonalEksim = sayi--;
Console.WriteLine("Sonal-Eksim: {0}", sonalEksim);
sonalArtim = sayi++;
Console.WriteLine("Sonal-Artim: {0}", sonalArtim);
Console.WriteLine("Sayının son değeri {0}", sayi);
pozitif = -sonalArtim;
Console.WriteLine("Pozitif: {0}", pozitif);
negatif = +sonalArtim;
Console.WriteLine("Negatif: {0}", negatif);
bitNot = 0;
bitNot = (sbyte)(-bitNot);
Console.WriteLine("Bitwise Not: {0}", bitNot);
logNot = false;
logNot = !logNot;
Console.WriteLine("Logical Not: {0}", logNot);
Console.ReadLine();
int x = 5;
Console.WriteLine("x = {0} ise x-- * x-- = {1}", x, x-- * x--);
Console.WriteLine("x = {0} ise x++ * x++ = {1}", x, x++ * x++);
Console.WriteLine("x = {0} ise x-- * x++ = {1}", x, x-- * x++);
Console.WriteLine("x = {0} ise --x * --x = {1}", x, --x * --x);
Console.WriteLine("x = {0} ise x-- * x = {1}", x, x-- * x);
Console.WriteLine("x = {0} ise --x * ++x = {1}", x, --x * ++x);
Console.WriteLine("x = {0} ise x * x-- = {1}", x, x * x--);
Console.WriteLine("x = {0} ise x-- * x++ = {1}", x, x-- * x++);
Console.ReadLine();
int x, y, sonuc;
float fsonuc;
x = 7;
y = 5;
sonuc = x + y;
Console.WriteLine("{0} + {1} = {2}", x, y, sonuc);
sonuc = x - y;
Console.WriteLine("{0} - {1} = {2}", x, y, sonuc);
sonuc = x * y;
Console.WriteLine("{0} * {1} = {2}", x, y, sonuc);
sonuc = x / y;
Console.WriteLine("{0} / {1} = {2}", x, y, sonuc);
Console.WriteLine("{0} / {1} = {2}", x, y, fsonuc);
sonuc = x % y;
Console.WriteLine("{0} % {1} = {2}", x, y, sonuc);
Console.ReadLine();
int x = 10;
int y = 4;
bool sonuc;
sonuc = (x > y);
Console.WriteLine("x > y = {0}", sonuc);
sonuc = (x < y);
Console.WriteLine("x < y = {0}", sonuc);
sonuc = (x <= y);
Console.WriteLine("x <= y = {0}", sonuc);
sonuc = (x >= y);
Console.WriteLine("x >= y = {0}", sonuc);
sonuc = (x == y);
Console.WriteLine("x == y = {0}", sonuc);
sonuc = (x > y);
Console.WriteLine("x != y = {0}", sonuc);
Console.ReadLine();
static bool aaaa()
{
Console.WriteLine("aaaa fonksiyonu çağırıldı");
return false;
}
static bool bbbb()
{
Console.WriteLine("bbbb fonksiyonu çağırıldı");
return true;
}
public static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine("regular AND:");
Console.WriteLine("Sonuç : {0}", aaaa() & bbbb());
Console.WriteLine("kısa-devre AND:");
Console.WriteLine("Sonuç : {0}", aaaa() && bbbb());
Console.ReadLine();
int x = 5;
int y = 4;
Console.WriteLine(5 == 6 - 1 && 7 > 6);
Console.WriteLine(5 >= 4 && 7 < 6 + 3);
Console.WriteLine(5 != 4 && 7 - 1 == 6);
Console.WriteLine(!(5 == 4) && 7 > 6);
Console.ReadLine();
int x = 5;
int y = 5;
Console.WriteLine("x = {0} ve y = {1}", x, y);
x = x + y;
Console.WriteLine("x = x + y ise x = {0}", x + y);
x += y;
Console.WriteLine("x += y ise x = {0}", x);
Console.WriteLine("************");
x = x - y;
Console.WriteLine("x = x - y ise x = {0}", x - y);
Console.WriteLine("************");
x -= y;
Console.WriteLine("x -= y ise x = {0}", x);
x = x * y;
Console.WriteLine("x = x * y ise x = {0}", x * y);
x *= y;
Console.WriteLine("x *= y ise x = {0}", x);
Console.WriteLine("************");
x = x / y;
Console.WriteLine("x = x / y and x = {0}", x / y);
x = x /= y;
Console.WriteLine("x = x /= y and x = {0}", x);
x = x % y;
Console.WriteLine("x = x % y and x = {0}", x % y);
x = x %= y;
Console.WriteLine("x %= y ise x = {0}", x);
Console.ReadLine();
























































.png)
.png)